May 22, 2024
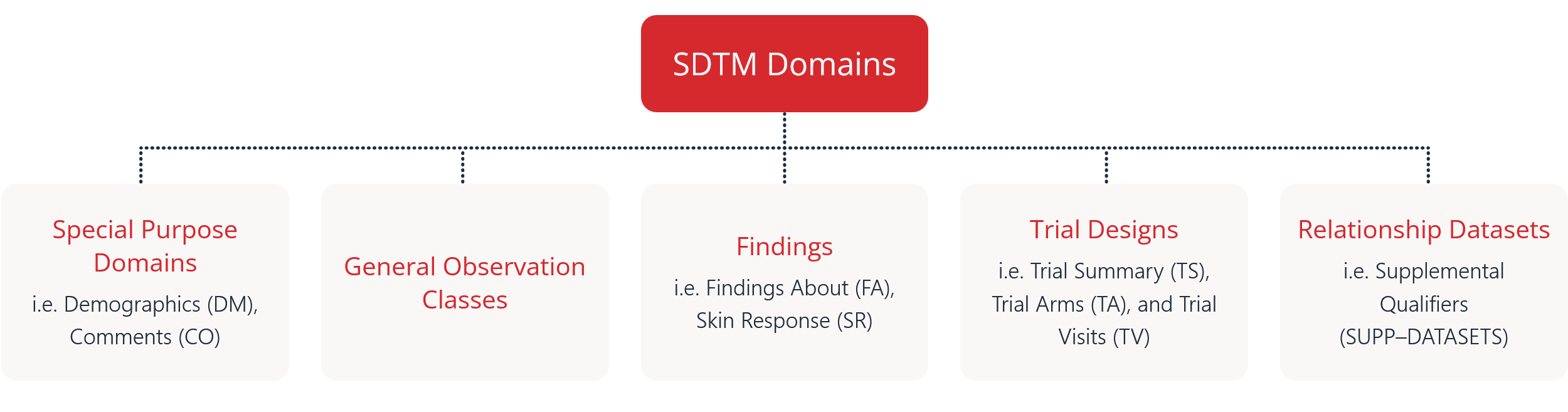
i.e. Demographics (DM), Comments (CO)
i.e. Findings About (FA), Skin Response (SR)
i.e. Trial Summary (TS), Trial Arms (TA), and Trial Visits (TV)
i.e. Supplemental Qualifiers
(SUPP–DATASETS)
Ready to start implementing SDTM?
Download our free best practice guide and become an expert in CDISC SDTM! You’ll learn how to avoid the pitfalls – and what you can do to address 5 common implementation challenges – with best practice steps to help you achieve compliant submissions.

Solutions Consultant
Ed Chappell has been working as a Solutions Consultant with Formedix, now part of Certara, for over 15 years, and has 22 years’ experience in data programming. He authored and presents our training courses for SEND, SDTM, Define-XML, ODM-XML, Define-XML and Dataset-XML.
Ed was heavily involved in the development of our dataset mapper and works closely with customers on SDTM dataset mapping. As an expert in clinical data programming, Ed also supports customers with Interim Analysis (IA) SDTM and FDA SDTM clinical trial submissions.
This article was originally written by Nathan Teuscher in October 2013, and was updated in May 2024 for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
Schedule a consultation with Certara
FAQs
Why are CDISC standards important for clinical trials?
CDISC standards improve data quality, streamline trial submissions, and are required by regulatory agencies like the FDA and PMDA. They enhance transparency, reduce errors, and speed up the review process.
How do SDTM datasets support FDA submissions?
SDTM datasets provide a consistent format that regulatory reviewers can quickly navigate. They help standardize safety and efficacy data, making submissions more efficient and reducing the risk of rejection due to formatting issues.
How is SDTM different from ADaM?
SDTM structures raw trial data into a standard format for regulatory review, while ADaM prepares analysis-ready datasets for statistical outputs. Both are CDISC standards but serve distinct purposes in the submission lifecycle.