April 11, 2025
Attain FDA Label Claims for Kinase Inhibitor Drugs with the Simcyp™ Simulator
We’ve compiled insights showcasing how numerous pharma and biotech companies have successfully replaced clinical studies with the Simcyp Simulator. This innovative approach has not only predicted clinical outcomes but has also played a pivotal role in achieving label claims.
The Final Product
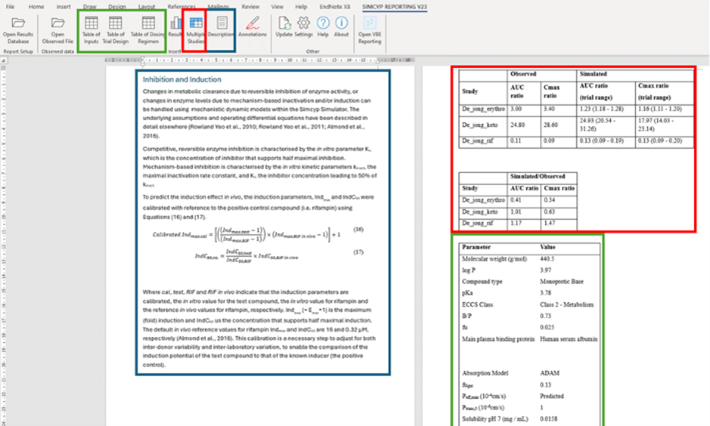
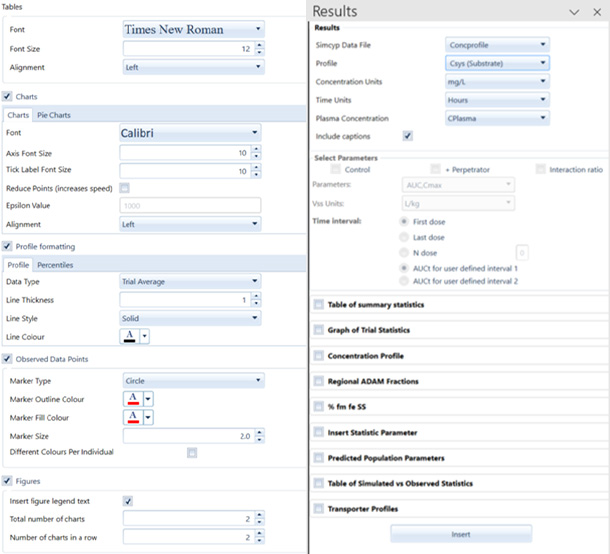
Interested to find out more about the Simcyp Report Assistant? Watch our latest technical webinar series where more details are provided and the Report Assistant is used to construct a report for Ibrutinib, one of the Simcyp Simulator library compounds.


Research Associate
Harry Moore is an Associate Research Scientist in Certara’s Simcyp team. Harry joined Certara in January 2021 as part of the translational science team. During this time, he has been involved in updating and adding compounds for Simcyp’s compound library, the Report Assistant word plug-in, Simcyp’s data management, developing organ-impaired populations.
1 FDA- Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Analyses – Format and Content 09/03/18
2 Guideline on the reporting of physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modelling and simulation. EMA/CHMP/458101/2016.
PBPK modeling software you can trust
Schedule a demo or consultation to see how the Simcyp PBPK Simulator can empower your team.