In the pharmaceutical industry, the end of a product’s patent protection, known as the loss of exclusivity (LoE), marks a significant turning point. It’s a period fraught with challenges as companies face the entry of generic competitors to the market, which can drastically reduce market share and revenue. Understanding the dynamics of LoE, particularly the so-called “patent cliff,” is essential for companies to navigate this phase successfully. In this blog post, we will explore what LoE is, explain the concept of the pharmaceutical patent cliff, discuss the challenges companies face as their products near the end of exclusivity, and outline strategies for defending market share in this critical period.
What is Loss of Exclusivity?
Loss of exclusivity occurs when a pharmaceutical product’s patent protection expires, opening the market to generic competitors. Patents give companies exclusive rights to sell a drug for a set period, typically 20 years from the date of filing. However, this period includes the time it takes for clinical trials and regulatory approval, so the effective market exclusivity is often much shorter. Once the patent expires, generic manufacturers can produce and sell cheaper versions of the drug, which leads to a significant drop in sales for the original product.
What is the Pharmaceutical Patent Cliff?
The patent cliff refers to a dramatic revenue drop that occurs when several major drugs lose their patent protection around the same time. This phenomenon can have a profound impact on a pharmaceutical company’s financial health. A historical example from the early 2010s saw blockbuster drugs like Lipitor and Plavix losing their exclusivity, leading to a significant reduction in revenue for their manufacturers. The term “patent cliff” conveys the image of a sudden drop, representing the rapid decline in sales as generics gain market share.
This period can be especially challenging for companies that have relied on blockbuster drugs. However, it also offers an opportunity to rethink market strategies, develop innovations, and explore ways to continue delivering value to patients and healthcare systems.
Challenges for Companies Facing Loss of Exclusivity
When a product approaches the end of its patent protection, pharmaceutical companies face several significant challenges:
1. Revenue Erosion:
Pharmaceutical companies face significant revenue erosion after losing exclusivity, as generics enter the market and reduce sales. For example, Pfizer’s Lipitor saw its revenue drop to less than 10% of its peak after losing its patent. This pattern of revenue erosion forces companies to explore strategies like creating generics themselves or maximizing value before exclusivity ends
2. Increased Competition:
With the entry of generics, the market becomes more competitive. The original brand may need to adjust pricing strategies to remain competitive, which can affect profit margins. In some cases, the market becomes saturated with multiple generics, intensifying the pressure.
3. Market Share Decline:
Generic drugs often capture a significant portion of the market shortly after launch, leading to a rapid shift in market dynamics.
4. Complex Supply Chains:
For biologics and other complex therapies, maintaining supply chain integrity is crucial. These products often require sophisticated manufacturing processes and cold-chain logistics, which can present challenges for originators in ensuring consistent supply at a lower scale.
5. Specialized Markets:
Many of the drugs approaching LoE today are specialized therapies, such as targeted treatments for rare diseases or biologics. These therapies serve smaller patient populations, requiring tailored approaches to maintain market presence.
Strategies for Defending Market Share
As pharmaceutical products approach the end of their exclusivity, companies have several proactive strategies to maintain their market presence and continue delivering value to healthcare providers and patients. These strategies can be organized into research-driven innovations, commercial initiatives, and execution tactics.
Research and Development solutions:
By exploring new therapeutic uses or seeking additional protections like pediatric exclusivity, companies can extend the life of their innovations. This allows them to continue serving patients while further developing the product’s potential benefits. In addition, companies can build on the success of their original product by introducing improved formulations, like extended-release versions, or even transitioning the drug to over-the-counter status. These enhancements help maintain the product’s relevance and expand its reach.
Commercial solutions
Launching branded generics or licensed versions of the original product enables companies to diversify and compete in the generic space, while still offering trusted, high-quality treatments. Developing patient-centric programs, such as those that improve access, adherence, and outcomes, creates added value beyond the medication itself. Companies can work closely with payers to offer value-based agreements, rebates, or outcome-driven pricing models. This collaborative approach highlights the full value of the product, focusing on patient outcomes, clinical effectiveness, and long-term satisfaction, rather than price alone.
Execution tactics
Omni-channel approaches play a key role in ensuring consistent and personalized communication, allowing companies to deliver value-driven messages across multiple platforms. By engaging stakeholders through a combination of digital, in-person, and remote tools, omni-channel execution ensures that the product’s value is clearly articulated at every touchpoint and that stakeholders receive enhanced experiences. Let’s explore how these strategies can be grouped and how omni-channel fits into this framework:
- Extending a product’s life through new indications or formulations requires clear communication of these innovations. An omni-channel approach ensures stakeholders receive research findings in engaging formats, whether through webinars, reports, or interactive presentations, making complex data more accessible.
- Enhancing existing products, like developing extended-release versions, needs strong messaging to highlight their clinical benefits. Omni-channel strategies ensure this message reaches providers, regulators, and patients through tailored channels, making research findings more impactful.
- Diversifying by launching branded or licensed generics requires clear differentiation in the market. Omni-channel communication ensures consistent messaging across multiple platforms, highlighting the quality and trust in these products to all stakeholders, from payers to patients.
- Patient-centric programs create significant value, but effective communication is key. Omni-channel strategies allow companies to engage patients and providers through various platforms, ensuring that support programs are clearly understood and easily accessible.
- Collaboration with payers relies on showcasing value-based agreements effectively. Omni-channel marketing allows for personalized presentations that meet payer needs, delivered through flexible channels like remote meetings or digital tools, ensuring timely and relevant discussions.
Omni-channel marketing engages stakeholders across multiple touchpoints, ensuring they receive the right information through the right channels—whether via digital platforms or direct engagements—reinforcing the product’s value in a competitive market. Interactive tools offer personalized content that resonates with providers, payers, and patients.
Leveraging Digital Tools for Optimal Omni-channel execution
In this digital age, stakeholders expect more than just traditional communication; they seek engaging, interactive, and tailored experiences. Omni-channel strategies ensure that companies deliver consistent messaging across various platforms, but to truly stand out, advanced digital tools are essential for delivering value-driven communication. These tools need to go beyond static presentations or simple reports. Stakeholders should be able to engage with the data directly, accessing the content in formats that suit their needs and preferences.
For example, some stakeholders might prefer accessing information through embedded content on a website, while others benefit from more tailored experiences such as mobile or web apps. These platforms need to be flexible, offering a variety of content types, from clinical trial data and animations to interactive models and live calculations. Furthermore, tools that allow stakeholders to manipulate data or run their own scenarios—such as calculating cost-effectiveness in real-time—provide a higher level of engagement and decision support.
In addition to these capabilities, it is vital that these platforms offer a comprehensive range of distribution methods. This might include stakeholder portals, interactive presentations, or even data-gathering tools that enable companies to refine their communication strategies based on stakeholder feedback. By allowing different levels of interaction and personalizing the delivery of information, companies can ensure that every stakeholder, whether a healthcare provider, payer, or patient, is fully engaged and informed.
Advanced tools like these are crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of omni-channel strategies. They ensure that stakeholders not only receive consistent messaging across all platforms but also experience a level of engagement that drives deeper understanding and trust.
BaseCase is designed to meet these exact needs, offering a versatile platform for distributing diverse content and enabling real-time interaction with data. Through web portals, apps, and interactive presentations, BaseCase ensures that value-driven messages are delivered in an engaging, tailored format, enhancing the overall communication experience across multiple channels.
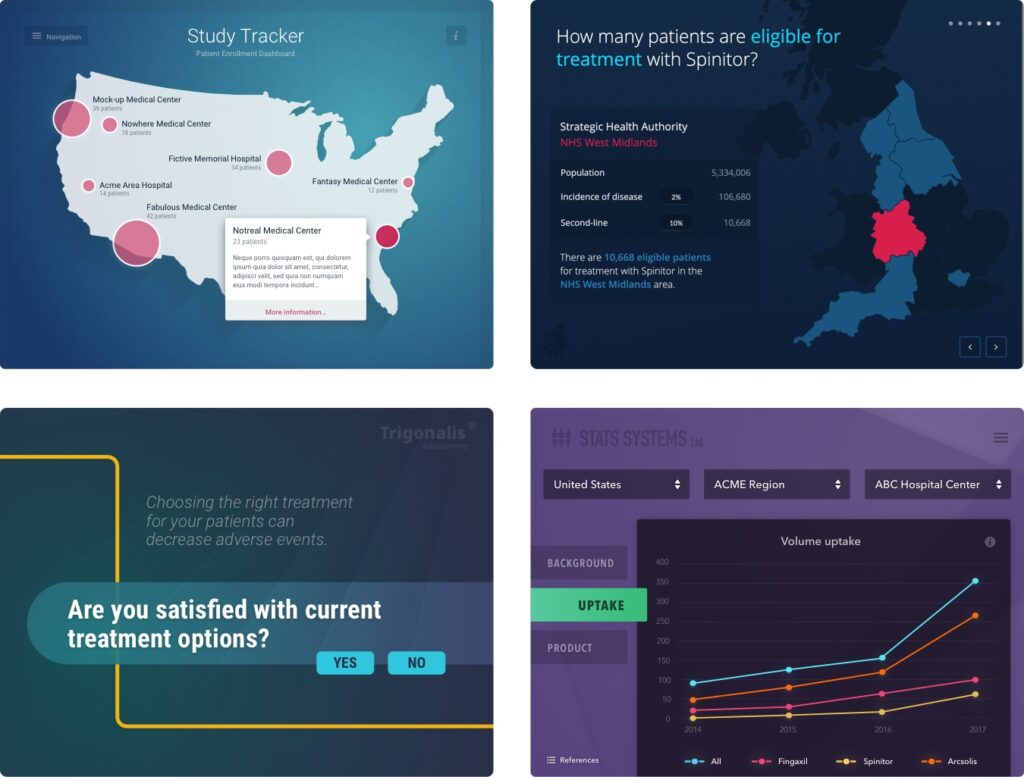
Sustaining Product Value and Market Share Post-LoE with BaseCase’s Digital Solutions
As pharmaceutical products approach Loss of Exclusivity (LoE), communicating the ongoing value of these innovations is essential for continuing to support healthcare providers and patients. By employing omni-channel strategies and advanced digital tools, companies can effectively share research-driven advancements and commercial solutions that extend product benefits, improve patient outcomes, and differentiate their offerings in competitive markets.
Click the button below to watch a webinar where we further explore how to navigate the pharmaceutical patent cliff.